Surface Passivation in Semiconductors
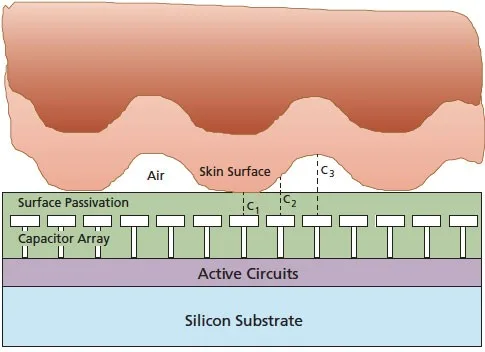
Surface passivation refers to a process of protecting the surfaces of semiconductor materials from external contaminants and unwanted interactions by applying a layer or coating

Surface passivation refers to a process of protecting the surfaces of semiconductor materials from external contaminants and unwanted interactions by applying a layer or coating
Advanced packaging refers to the techniques used to package a microchip or semiconductor device in a compact and reliable way.

Microbumps are small, raised metal bumps or spheres that connect the chip with the printed circuit board (PCB). In multichip modules they also connect the different layers of the chip.
FOWLP stands for Fan out wafer level packaging, which is a type of chip packaging technology in the semiconductor industry.

A NOR gate is a logic gate that performs a Boolean operation on its input signals.

A defect refers to any physical or chemical imperfection in the crystal lattice structure that can affect the electrical or optical properties of a semiconductor device.
A semiconductor is a type of material that has an electrical conductivity between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass.