
Fluxless TCB vs TCB
As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
ZnO, or Zinc Oxide, is a special type of material used in semiconductors. It is made up of zinc and oxygen atoms bonded together. ZnO has unique properties which make it suitable for different applications in electronics.
In semiconductors, ZnO is used to create electrical components that can control and manipulate the flow of electricity. It acts as a semiconductor material, which means it can conduct electricity under certain conditions. By adjusting the composition and structure of ZnO, engineers can create different types of electronic devices such as transistors, diodes, and sensors.
One of the key characteristics of ZnO in semiconductors is its ability to convert electrical energy into light and vice versa. This property makes ZnO ideal for optoelectronic devices, such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LEDs contain ZnO. When you connect the LED to a power source and electric current flows through it, the electrons in the ZnO get excited. Once electrons cool down, they release energy in the form of tiny light particles called photons. LEDs find many applications, including lighting, displays, and communication systems.
ZnO also has high transparency to visible light, which means it can transmit light very effectively. This makes it suitable for applications where transparent materials are needed, such as in solar cells or displays.
In addition to its electrical and optical properties, ZnO is also well-known for its mechanical strength and stability, making it a reliable material for semiconductor devices. Its wide bandgap allows it to operate at high temperatures and in harsh environmental conditions.
Overall, ZnO is an important material in the field of semiconductors, enabling the development of various electronic devices with its unique properties.

Illustrative Case Study: ZnO in Thin-Film Transistors (TFTs)
In this case study, researchers aimed to investigate the feasibility of using zinc oxide as the semiconductor material in thin-film-transistors, TFTs, for display applications. They wanted to determine if ZnO could offer advantages over traditional silicon-based TFTs, such as improved performance, cost-effectiveness, and ease of manufacturing.
Conclusion First:
The case study demonstrated that zinc oxide has the potential to be a viable semiconductor material for thin-film transistors in display applications. While challenges exist, ongoing research aims to overcome them and further optimize the performance of ZnO-based TFTs, potentially leading to more efficient and cost-effective electronic devices in the future.
Key Steps:
Material Deposition: The researchers deposited a thin layer of zinc oxide onto a substrate, forming the semiconductor layer of the Tft. They used a technique like sputtering or chemical vapor deposition to create a uniform layer.
Device Fabrication: The semiconductor layer was patterned to create the necessary transistor structure. This included defining the source, drain, gate, and channel regions.
Characterization: The electrical properties of the ZnO-based TFT were extensively characterized. This involved measuring parameters such as mobility (how quickly charge carriers move through the material), on-off ratio (the difference in conductivity between the on and off states), and threshold voltage (the voltage at which the transistor turns on).
Comparison: The performance of the ZnO-based TFT was compared to traditional silicon-based TFTs. Researchers looked at factors like switching speed, power consumption, and reliability.
Findings:
The researchers found that zinc oxide had several favorable properties for TFTs:
High Mobility: ZnO exhibited good charge carrier mobility, enabling fast switching speeds in the transistors.
Transparency: ZnO is transparent, which is beneficial for applications like transparent displays and touchscreens.
Flexibility: ZnO-based TFTs could potentially be used in flexible and bendable electronics due to the material’s mechanical properties.
Cost-Effectiveness: ZnO can be deposited using relatively simple and cost-effective techniques, which could lead to more affordable manufacturing processes.
Challenges:
However, the study also highlighted some challenges:
Stability: ZnO-based devices can be sensitive to environmental conditions, affecting their long-term stability.
Interface Quality: The interface between ZnO and other layers in the TFT structure can impact performance. Achieving a high-quality interface is crucial.
Interface Quality: The interface between ZnO and other layers in the TFT structure can impact performance. Achieving a high-quality interface is crucial.
Conclusion:
The case study demonstrated that zinc oxide has the potential to be a viable semiconductor material for thin-film transistors in display applications. While challenges exist, ongoing research aims to overcome them and further optimize the performance of ZnO-based TFTs, potentially leading to more efficient and cost-effective electronic devices in the future.
One major application field of ZnO is in electronic devices. It has excellent electrical properties, making it ideal for the manufacture of thin film transistors (TFTs). TFTs are essential components in modern displays such as flat panel displays (FPDs) and thin film photovoltaic panels (TFPVs). ZnO is used as the active layer in TFTs and has shown promising performance due to its high electron mobility and broad optical transmission. Another application of ZnO in electronics is in the field of light emitting diodes (LEDs), where it is used as a phosphor material. ZnO based phosphors have the potential to exhibit high brightness, long lifetime, and good color performance, which is essential in the manufacture of LEDs.
Zinc oxide (ZnO) also finds applications in the field of sensing, where it serves as a highly sensitive material for detecting various gases like methane and carbon monoxide. Air quality monitoring systems, automotive exhaust monitoring systems, and industrial safety systems also use zinc oxide
Zinc oxide (ZnO) holds significant potential in the field of biomedicine as well. ZnO nanoparticles exhibit excellent antibacterial properties, which researchers utilize in producing various medical devices like surgical masks, gloves, and other equipment.
Lastly it is making its mark in the field of energy. Researchers are employing it as an alternative to indium tin oxide (ITO) in producing photovoltaic cells because of its enhanced transparency and conductivity. Moreover, they have utilized ZnO nanowires as electrode material in dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). DSSCs are a type of thin film solar cell that can be manufactured at a lower cost than traditional silicon based solar cells.

As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
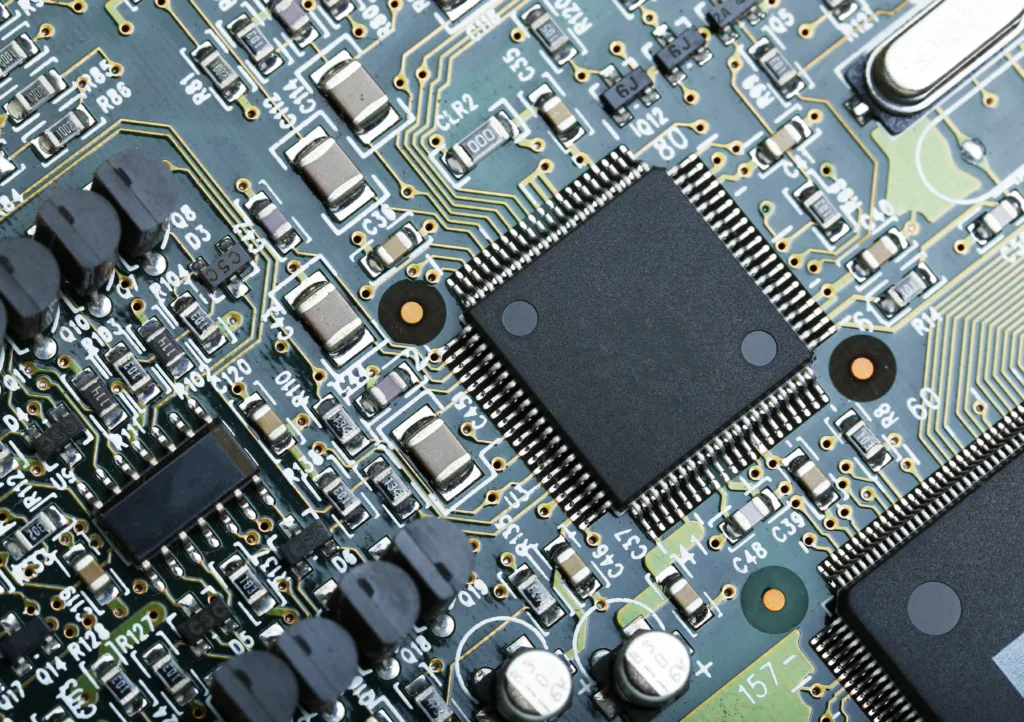
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
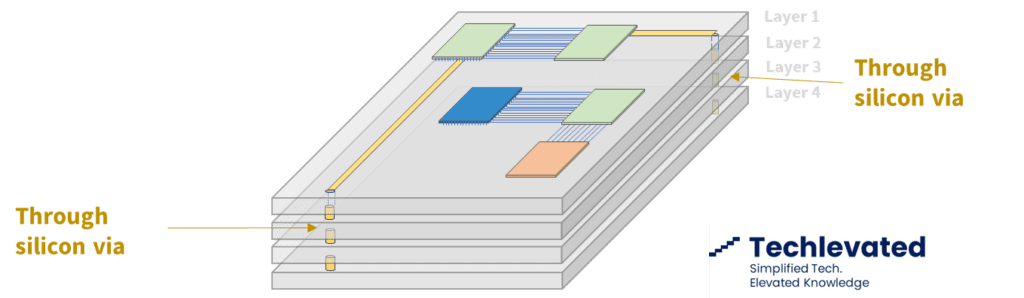
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
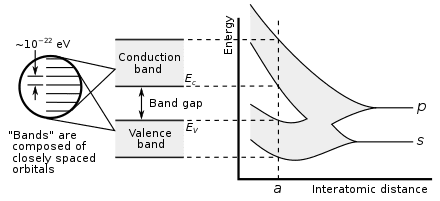
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
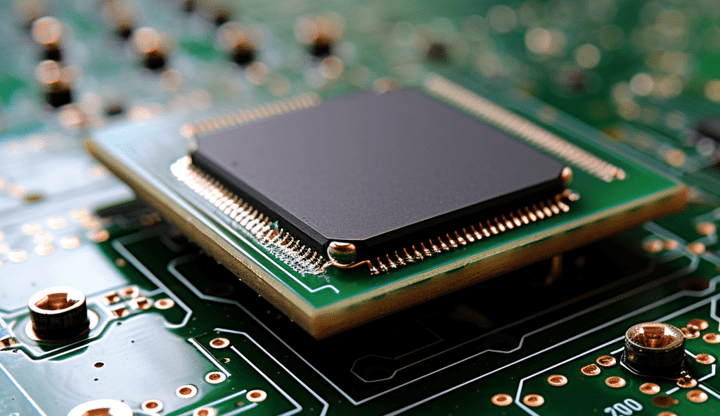
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.