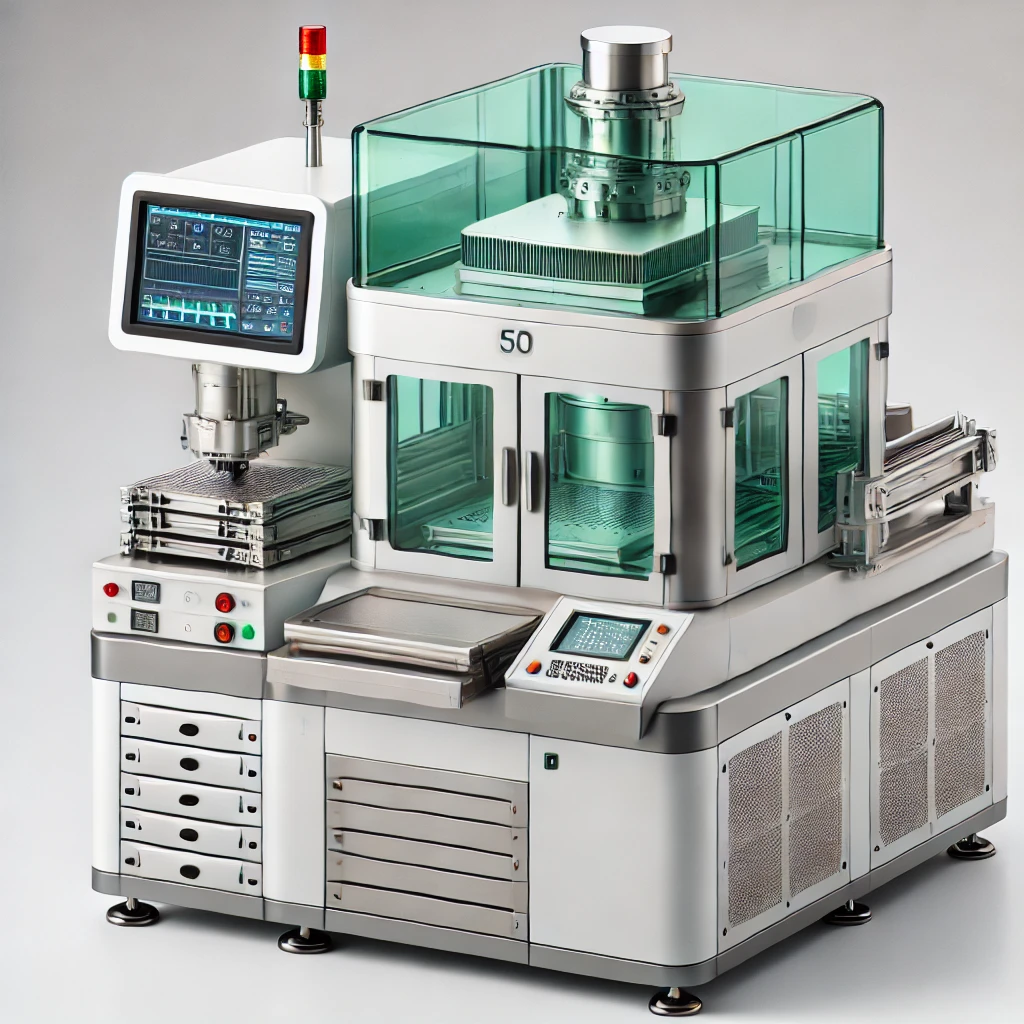

Fluxless TCB vs TCB
As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
Broadband refers to high-speed internet connections that are capable of transmitting large amounts of data simultaneously. Broadband includes various technologies such as DSL, coaxial cable, fiber optic, satellite and wireless.
DSL technology uses existing telephone lines to transmit data. DSL was widely used at the beginning of the 20th century but has been replaced by coaxial cable and fiber optic networks given it provides relatively low download speeds.
Cable broadband operates over the same infrastructure as cable television, providing high-speed internet access through coaxial cables. It can handle bandwidth-hungry activities like 4K video streaming and online gaming with ease. However, it can sometimes suffer from network congestion during peak usage hours.
Fiber optic broadband offers very high speeds, low latency and it is resistant to signal interference. Fiber is often considered the best standard in internet connections, making it perfect for 4K streaming, remote working or online gaming. Fiber optic networks require important infrastructure investments, so they might not be available everywhere.
Broadband serves as a catalyst for economic growth, driving innovation and fostering digital inclusion. It enables businesses to reach a broader customer base, promotes remote work opportunities, and facilitates e-learning initiatives by providing equal access to educational resources. Additionally, broadband plays a vital role in bridging the digital divide, ensuring that individuals in underserved areas have equal opportunities for education, healthcare, and economic empowerment.


As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
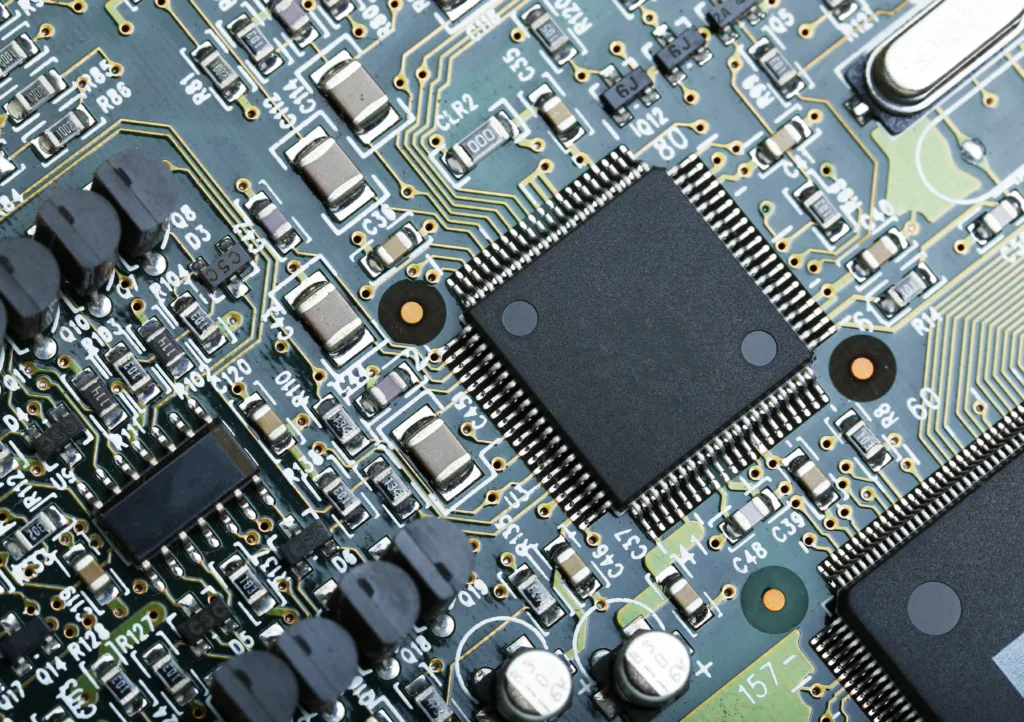
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
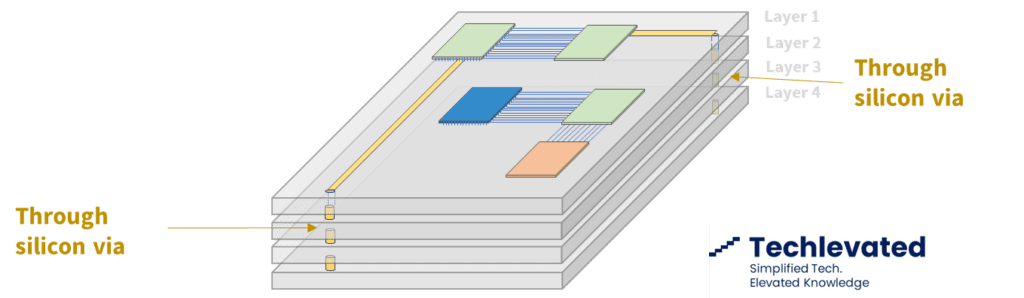
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
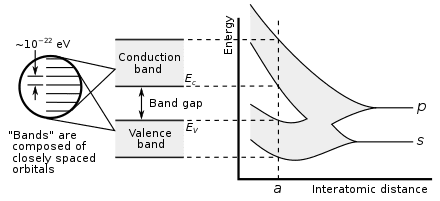
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
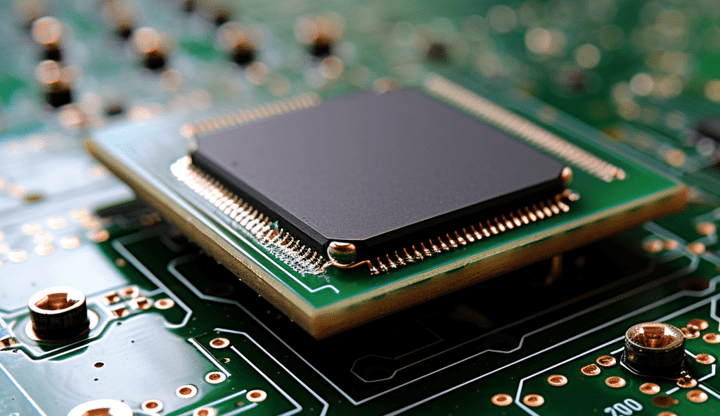
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.