
Fluxless TCB vs TCB
As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
Microbumps are small, raised metal bumps or spheres that connect the chip with the printed circuit board (PCB). In multichip modules they also connect the different layers of the chip. Microbumps are made of conductive materials, typically metals like copper. This reduces the resistance in the interconnects, ensuring that signals travel quickly and with minimal loss of energy.
They serve as conduits for electrical signals to travel from one part of the chip to another. This is essential for different components of the chip to communicate and coordinate their functions. With the increasing demand for smaller and more powerful electronic devices, microbumps enable the creation of high-density packaging. They allow for multiple layers of circuits to be stacked on top of each other, effectively maximizing the use of available space on the chip.
Efficient heat dissipation is crucial in semiconductor devices to prevent overheating. Microbumps can also serve as thermal interfaces, helping to transfer excess heat away from the chip.
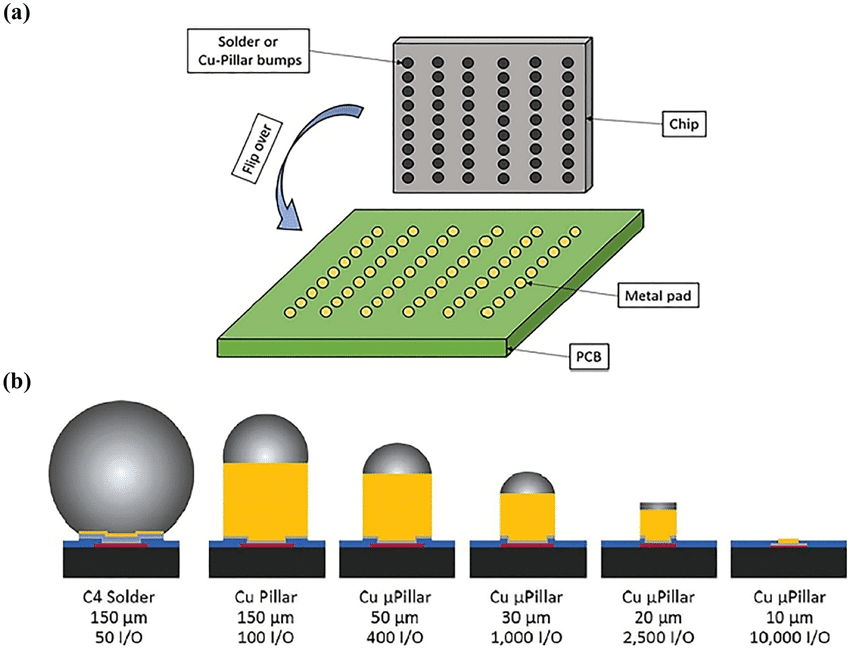
These tiny metal structures are typically measured in micrometers (µm, one-thousandth of a millimeter) or even nanometers (nm, one-millionth of a millimeter).
To put this into perspective, a microbump of 1µm would be smaller than the width of a human hair. In advanced semiconductor technology, microbumps can be even smaller, in the nanometer range. A microbump in the nm range would be in the scale of atoms and molecules, making them extremely small.

As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
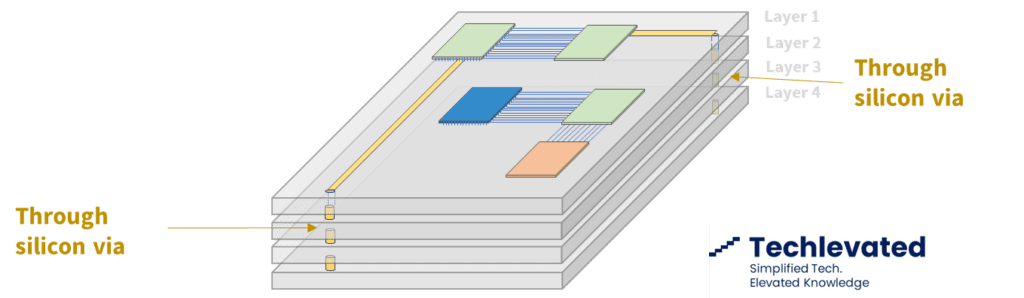
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
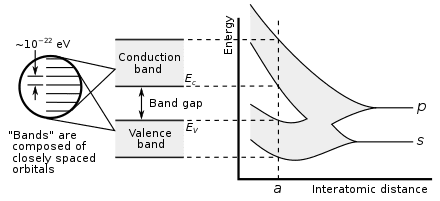
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.