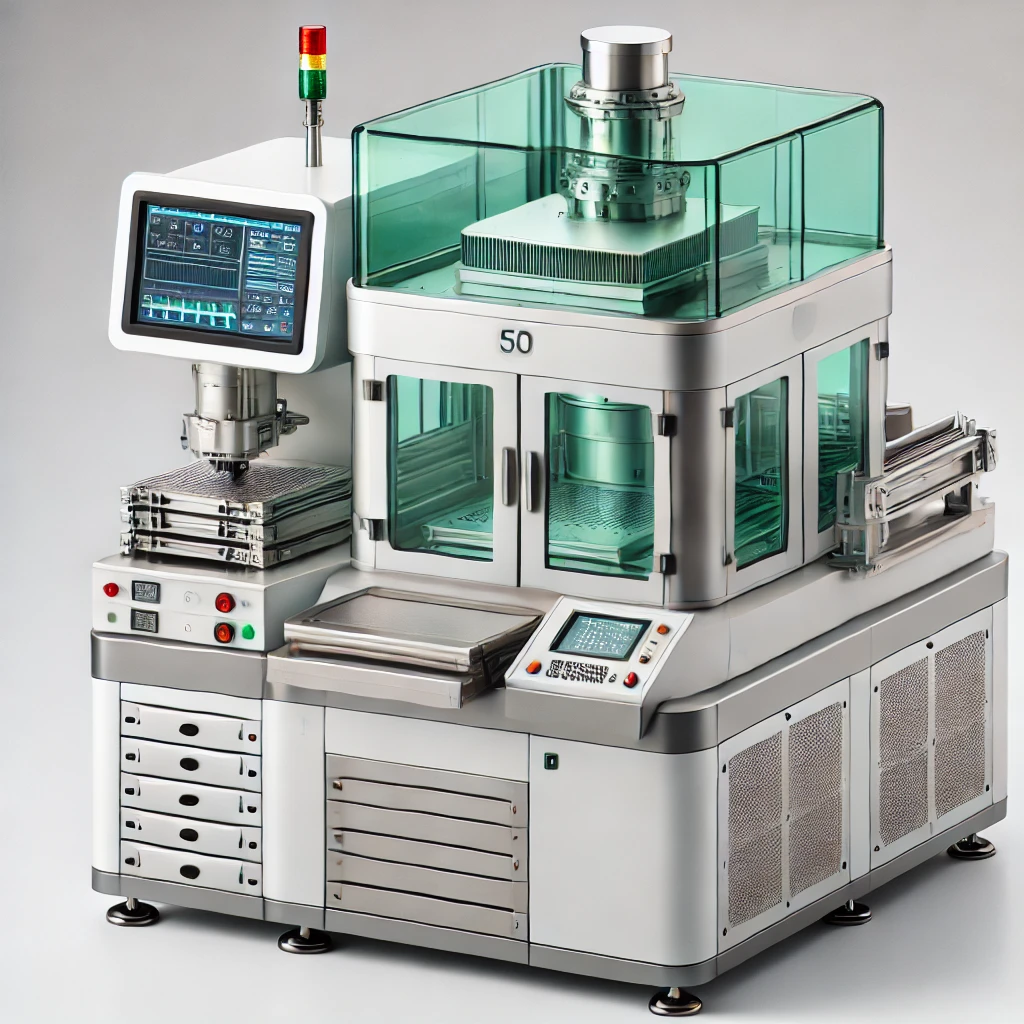

Fluxless TCB vs TCB
As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
A Nor gate is a logic gate that performs a Boolean operation on its input signals. It is an important building block in digital electronics. Its name means “NOT OR gate”, as it only gives a “true (1)” value when all of its inputs are “false (0)”
A NOR gate has two or more inputs and one output. It works by taking the inputs and producing an output based on their values. If any of the inputs is a “1” (which means electricity is flowing), then the output will be a “0” (which means no electricity is flowing). But if all the inputs are “0”, then the output will be a “1”.
One way to think about a NOR gate is by imagining a light switch. If you have multiple switches controlling a light bulb, the light bulb will only turn off if all the switches are turned on. But if any of the switches are turned off, the light will turn on.
NOR gates are used in many common electronic devices like computers or calculators to perform logical operations and make decisions based on the input values.
Truth Table of a NOR Gate:
| A (Input) | B (Input) | Y (Output) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NOR gate and NAND gates are two fundamental logic gates used in digital electronics. They have opposite logic behaviors:
Truth Table:
| A (Input) | B (Input) | Y (Output) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Truth Table:
| A (Input) | B (Input) | Y (Output) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
In summary:

As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
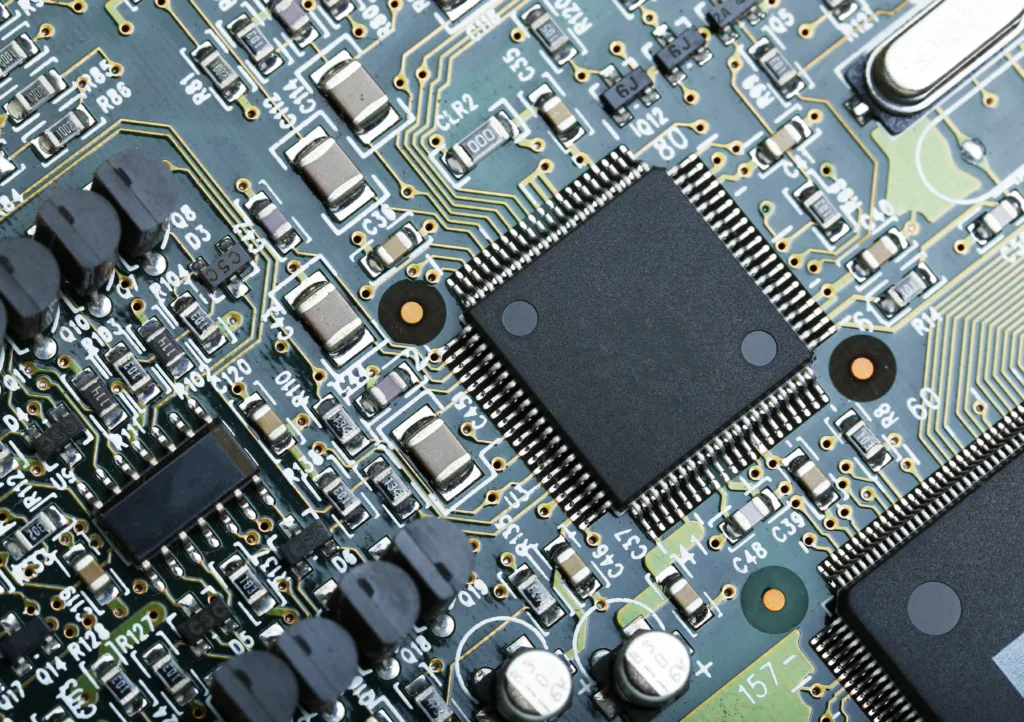
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
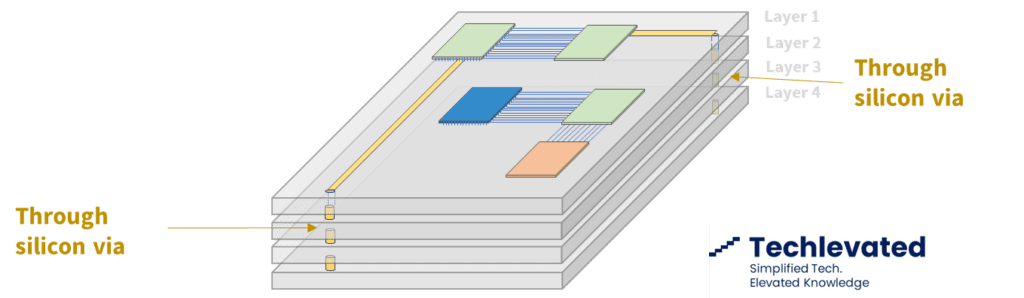
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
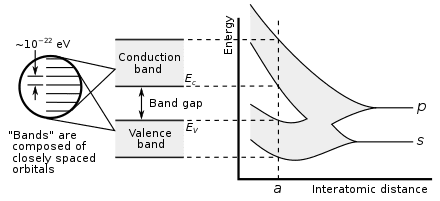
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
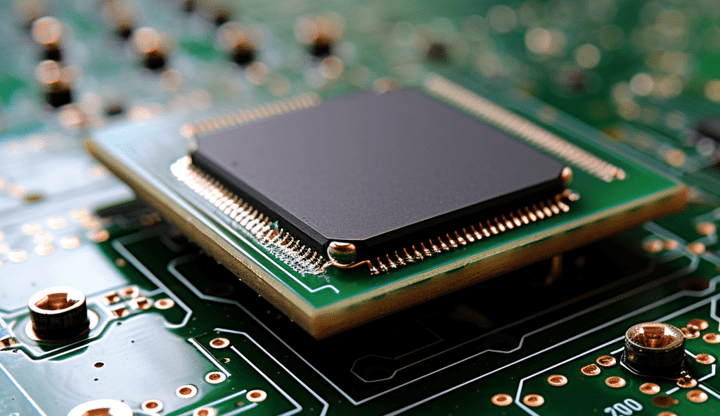
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.