802.11 standard (Wi Fi)
The 802.11 standard, commonly known as Wi fi, is a set of wireless communication protocols and technologies that enable devices to connect and communicate over a local area network (LAN) using radio signals
The 802.11 standard, commonly known as Wi fi, is a set of wireless communication protocols and technologies that enable devices to connect and communicate over a local area network (LAN) using radio signals
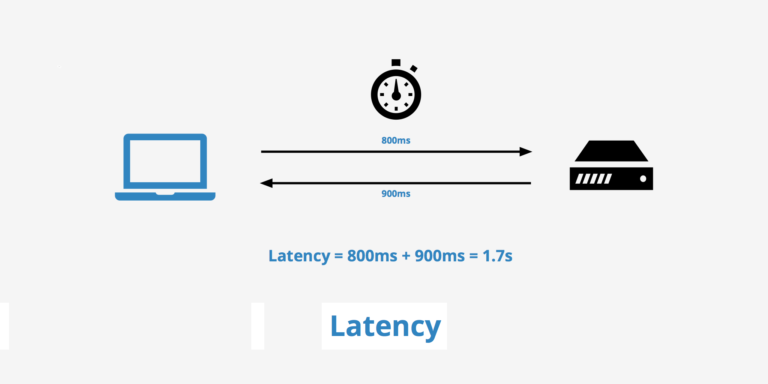
Network latency refers to the delay or amount of time it takes for information to travel from one point to another across a network.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a vast network of connected devices, objects, and systems that can interact with each other and exchange information using internet protocols.

Zinc Oxide, is a special type of material used in semiconductors. It is made up of zinc and oxygen atoms bonded together.

Broadband refers to high-speed internet connections that are capable of transmitting large amounts of data simultaneously. Broadband includes various technologies such as DSL, coaxial cable, fiber optic, satellite and wireless.
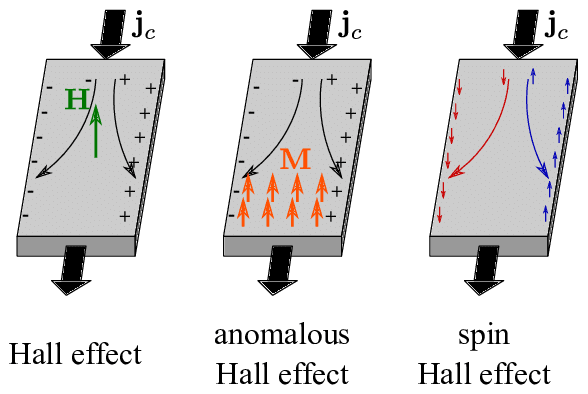
The Hall effect is a phenomenon observed in conductive materials, including semiconductors, when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the direction of current flow.
A Voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) is a type of electronic oscillator that produces an oscillating signal whose frequency can be tuned by an input voltage.
In semiconductors, a charge carrier is a particle that is either positively charged (called “holes”) or negatively charged (called “electrons”) that carries an electric charge through the semiconductor material.
In the field of semiconductors, an insulator, also known as a dielectric, is a material that does not conduct electricity.
Tape out refers to the process of transferring a final semiconductor design in the form of a computer aided design (CAD) file to a manufacturing facility for fabrication.