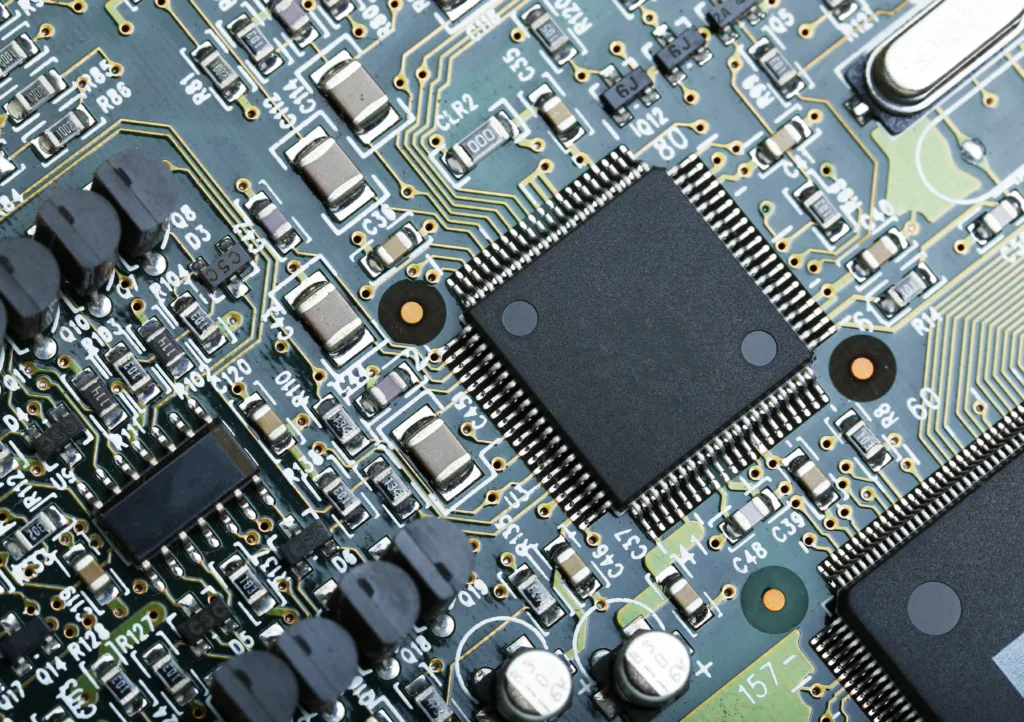
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a vast network of connected devices, objects, and systems that can interact with each other and exchange information using internet protocols. It involves the integration of physical devices, such as sensors, actuators, and smart devices, with the internet to enable them to collect and share data, and perform various tasks without human intervention.
In IoT, devices are equipped with sensors that can collect real time data from various sources, such as environmental conditions, user behavior, and machine operations. These devices are connected to the internet, allowing them to transmit and receive data to and from other devices, remote servers, or cloud based platforms. This data can be analyzed and processed to extract valuable insights, automate actions, and improve decision making processes.
IoT is revolutionizing industries by enabling diverse applications such as smart homes, smart cities, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, agriculture optimization, and transportation management. It offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, cost savings, enhanced safety and security, and improved quality of life.
To achieve seamless communication and connectivity, IoT relies on a variety of communication technologies such as Wi fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks, and Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs). These technologies enable devices to transmit and receive data wirelessly, often with low power consumption and extended range.
However, the widespread adoption of IoT also raises concerns about security, privacy, and data management. With billions of interconnected devices collecting and exchanging sensitive data, ensuring the privacy and security of this information becomes crucial. Solutions such as encryption, authentication, access control, and secure communication protocols are employed to safeguard data in IoT ecosystems.
In summary, the Internet of Things (IoT) represents a paradigm shift in the way we interact with technology and the world around us. By connecting physical objects to the digital realm, IoT opens up endless possibilities for innovation and efficiency in various industries.