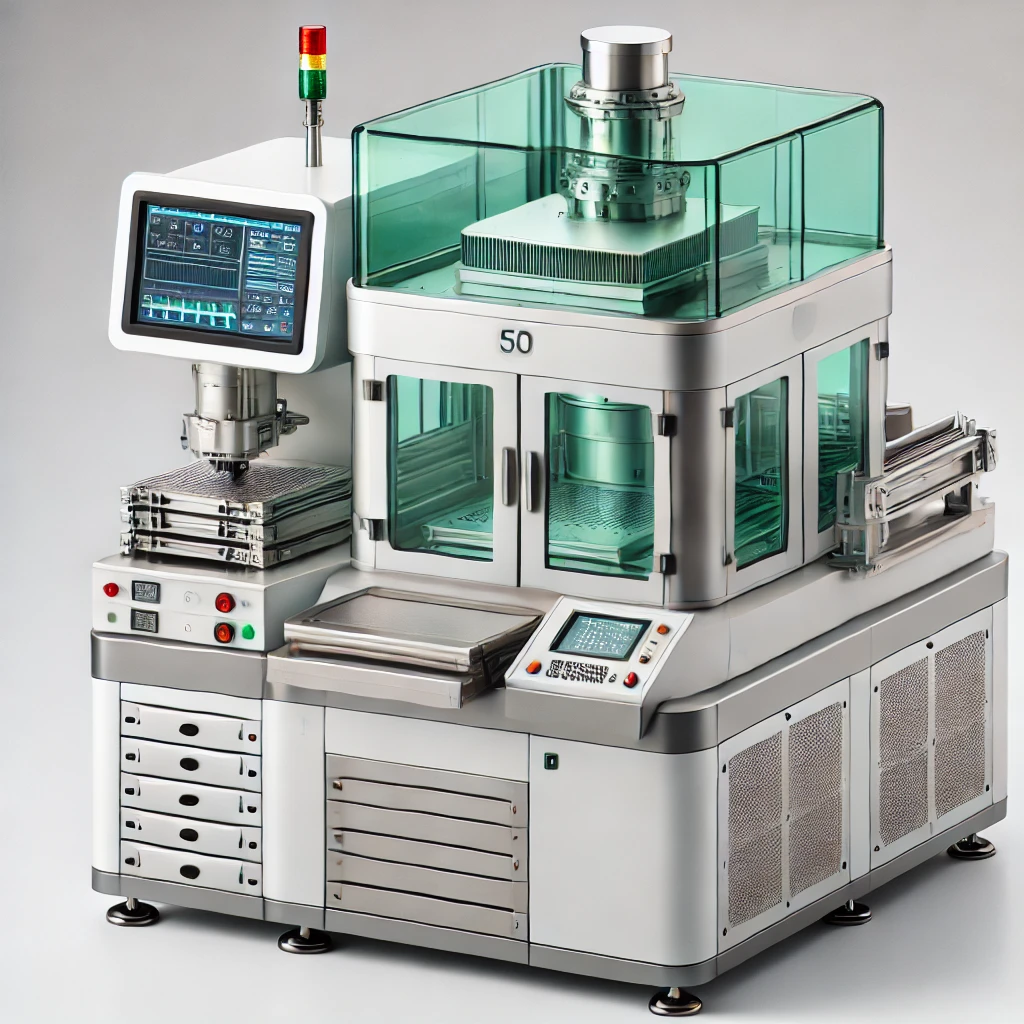

Fluxless TCB vs TCB
As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
A semiconductor is a material that possesses a unique ability to partially conduct electricity, making it neither a perfect conductor nor an insulator. It falls between metals, which efficiently conduct electricity, and insulators, which do not conduct at all. Semiconductors have a crucial role in electronic devices because their electrical conductivity can be easily controlled or modified by factors like temperature, voltage, or the introduction of impurities through a process called doping. This property allows semiconductors to act as the foundation for transistors, diodes, and other electronic components, enabling the precise control of electrical signals and the manipulation of data in countless modern technologies, including computers, smartphones, and microchips.
No, a semiconductor and a chip are not the same thing, but they are closely interrelated.
In simple terms chips, or integrated circuits, are fabricated on semiconductor materials. A semiconductor material has the electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (imagine copper or aluminium) and an insulator (think of rubber). Common semiconductor materials are silicon, gallium arsenide (GaAs) or germanium. A chip consists of a complex network of transistors, resistors, capacitors, and interconnections all etched onto a small piece of semiconductor material. These components work together to perform various functions, such as processing data, amplifying signals, or storing information.
Semiconductors are used in a vast amount of industries. Basically, every device that contains a chip is using semiconductors. The arrival of the internet, smartphones, personal computers and connected devices has caused exponential growth in the use of semiconductors in the past two decades. This growth is expected to continue as our society becomes more interconnected. According to Fortune Business Insights, the semiconductor industry is expected to grow at a 12% compounded annual growth rate until 2029.
Semiconductors are the foundation of modern electronics. Integrated circuits (ICs), commonly known as chips, are built on semiconductor substrates and act as the brain of electronic devices. Semiconductors enable the processing, storage, and transmission of information. Advancements in semiconductor technology allow for faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient electronic devices. Advances in semiconductor technology have led to the exponential growth in computing power, enabling complex calculations, data storage, and rapid data communication.
Semiconductors have also transformed the automotive industry. Modern vehicles include hundreds of chips and sensors making them safer and more efficient. Think of engine control, safety systems (like airbags and ABS), infotainment or advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
In healthcare, semiconductors power medical devices that save lives and improve patient care. These devices include pacemakers, insulin pumps, diagnostic equipment, and imaging machines like MRI scanners.
Furthermore, semiconductors contribute to sustainable technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, automation or aerospace.

As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
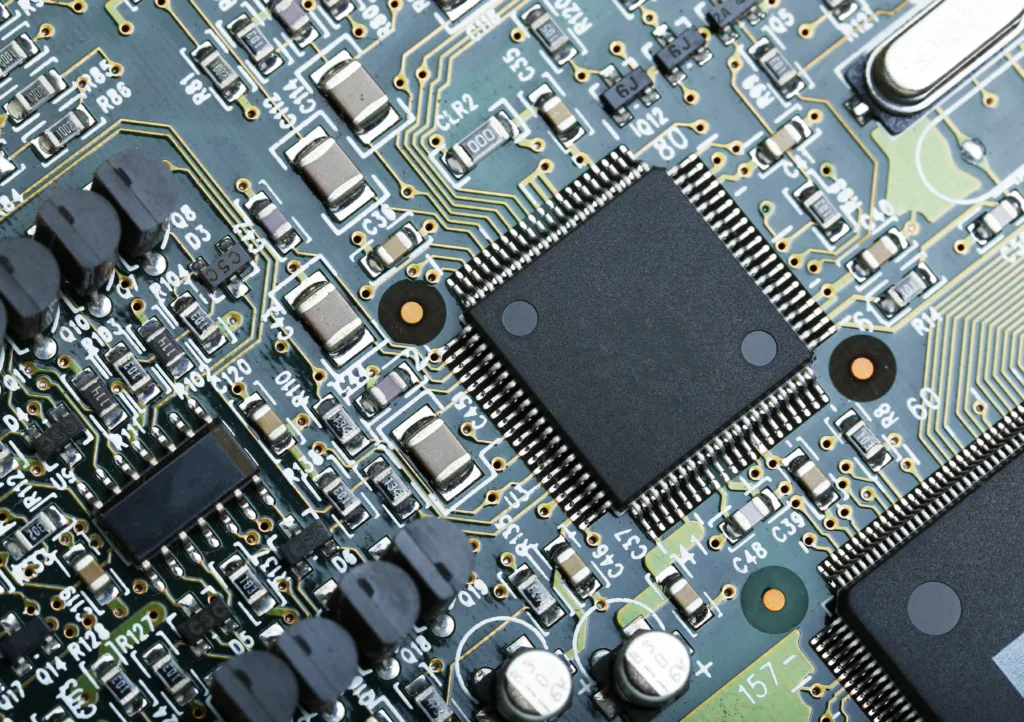
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
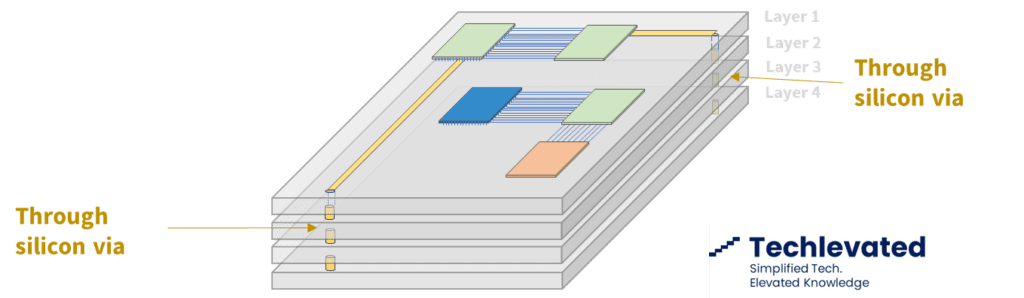
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
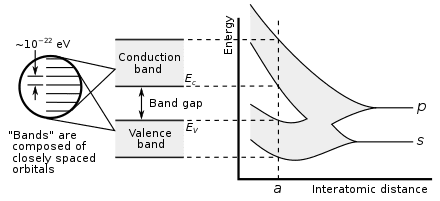
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
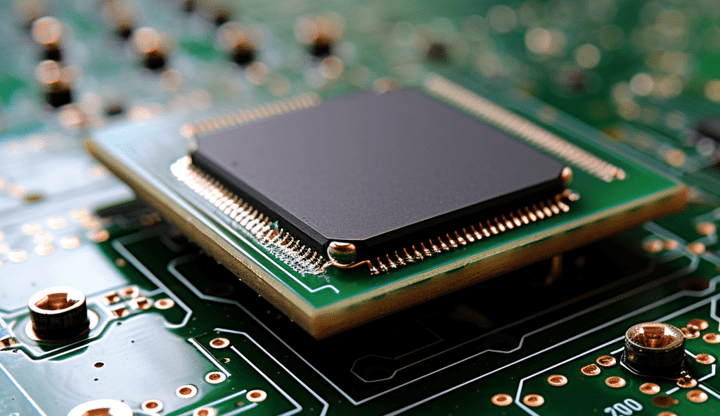
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.