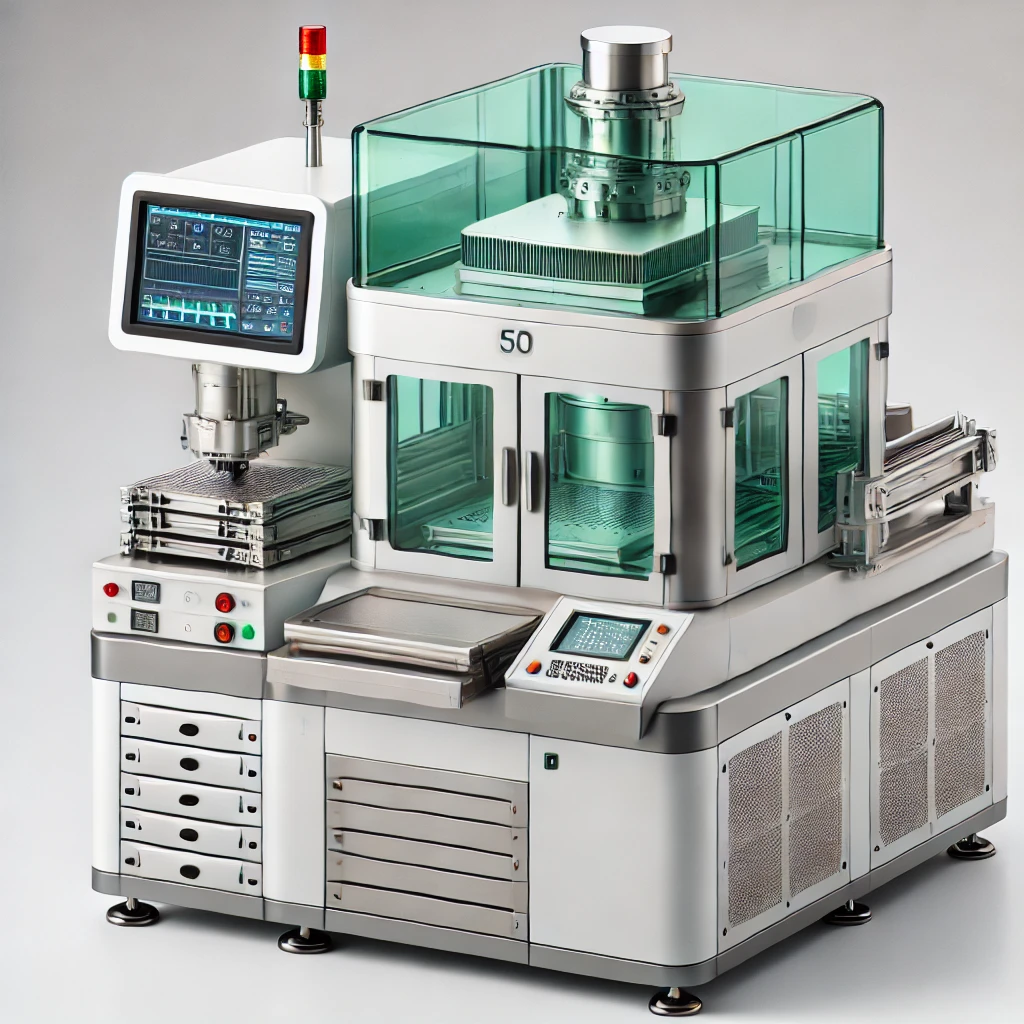

Fluxless TCB vs TCB
As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
Digital content delivery refers to the process of transmitting and distributing various forms of digital information, such as videos, music, and documents, from a source to users over a network. This content can be accessed and enjoyed by people all around the world through devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers.
Think of digital content as files or data that are stored and shared electronically. Instead of going to a physical store to buy a DVD or a CD, we can now download or stream movies and music directly from the internet to our devices. Digital content delivery makes it possible for us to access a wide variety of media instantly and enjoy it wherever we are.
The process of digital content delivery involves several steps. First, the content is created and stored on servers, which are powerful computers that hold and distribute the files. Then, when someone wants to access the content, their device sends a request to the server. The server then delivers the requested content to the user’s device. This can happen in real-time, as in the case of live streaming, or it can be downloaded and stored on the user’s device for later viewing.
Digital content delivery is fast and convenient because it relies on high-speed internet connections. It allows us to enjoy movies, music, and other media without having to physically possess a copy of it. We can simply stream it or download it when we want to enjoy it. This has revolutionized the way we consume content and has made it easier for us to discover and access a vast array of digital media.
So, in a nutshell, digital content delivery is all about making it easy for us to access and enjoy digital media like movies, music, and documents through our devices, using the internet as a means of delivery. It brings entertainment, information, and creativity right at our fingertips.

In the early 2010s, Netflix faced several challenges related to digital content delivery:
Solution: Netflix implemented several strategies to address these challenges:
Netflix’s case study demonstrates the importance of a robust content delivery infrastructure, content diversification, and data-driven personalization in the digital content delivery industry. By continually innovating and focusing on user experience, Netflix successfully transformed from a DVD rental service to a global streaming giant.
In the entertainment industry, digital content delivery has transformed the way we access and enjoy music, movies, TV shows, and other forms of media. Platforms like streaming services and online stores allow users to instantly access a vast library of content, eliminating the need for physical media and enabling on demand consumption. This has not only reshaped the way we consume media but has also created new revenue streams for artists, producers, and distributors.
The publishing industry has also greatly benefited from digital content delivery. E books and online platforms have made it possible for authors and publishers to distribute their works in a more cost effective and accessible manner. Users can now easily download and read books on various devices, expanding the reach of literature to a global audience.
In the education sector, digital content delivery has revolutionized the way knowledge is disseminated. Online learning platforms enable students to access educational materials, lectures, and interactive content from anywhere in the world. This has made education more accessible, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and convenience.
The news and media industry has experienced a profound shift with digital content delivery. Online news portals, blogs, and social media platforms have become major sources of news and information, influencing how we stay updated on current events. Real time news updates, multimedia content, and personalized recommendations have become staples of the digital news landscape.
The advertising and marketing industry has also seen significant changes due to digital content delivery. Advertisers can now reach their target audiences with tailored and personalized content through various digital channels. The ability to track and analyze user engagement allows for more effective targeting and optimization of advertising campaigns.
The gaming industry has embraced digital content delivery through online gaming platforms and app stores. Gamers can easily download and access a wide range of games, updates, additional content, and virtual purchases. This has transformed the gaming experience, enabling multiplayer interactions, online competitions, and constant updates to enhance gameplay.
Furthermore, industries such as healthcare, finance, government, and telecommunications rely on digital content delivery for various purposes. In healthcare, telemedicine platforms allow remote consultations and access to medical records. Financial institutions provide online banking and financial services, ensuring secure delivery of sensitive data. Government agencies utilize digital content delivery for e government services and information dissemination. Telecommunications companies facilitate the distribution of digital content through their networks, enabling seamless streaming, downloads, and communication.
Digital content delivery refers to the distribution of various forms of digital media, such as music, videos, documents, and software, over communication networks. Evolving significantly since the 1980s, digital content delivery has transformed the way content is consumed, shared, and monetized.
In the early 1980s, digital content delivery was primarily limited to physical media like floppy disks and CDs. However, with the rise of the internet, advancements in computing, and the increasing power of communication networks, the landscape began to change. The emergence of file transfer protocols, such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol), allowed for the transfer of digital files over interconnected computer networks.
By the 1990s, the World Wide Web became widely accessible, and the internet began to revolutionize digital content delivery. The introduction of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) enabled the seamless retrieval and display of web pages and media files. This shift in technology opened up new opportunities for businesses to distribute digital content directly to users’ computers.
The early 2000s witnessed a significant milestone with the advent of peer to peer (P2P) file sharing. Platforms like Napster, Bittorrent, and LimeWire enabled users to share and download digital content directly from one another’s devices. This decentralized approach challenged traditional content distribution models, leading to legal debates around copyright infringement and the unauthorized sharing of copyrighted material.
The mid 2000s marked a pivotal moment with the rise of digital content platforms and online stores. Companies like Apple with iTunes and Amazon with its digital music store started offering legal ways to purchase and download music, signaling a shift towards legitimate digital content distribution.
The subsequent years brought further advancements in streaming technologies. With the widespread availability of broadband internet connections, streaming services like YouTube, Netflix, and Spotify gained popularity. Content delivery networks (CDNs) played a crucial role in ensuring seamless delivery of media by caching and distributing content from geographically distributed servers closer to the end users.
More recently, the proliferation of mobile devices and the advent of high speed mobile networks have fueled the growth of digital content delivery. Streaming platforms have become ubiquitous, offering not only music and videos but also podcasts, audiobooks, and various forms of digital publications.
Today, digital content delivery continues to evolve rapidly. The focus has shifted towards personalized content recommendations, improved user experiences, and the expansion of digital rights management to protect intellectual property. Additionally, emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are reshaping the way digital content is created, delivered, and consumed.

As interconnection pitches shrink below 10µm for advanced logic and memory applications, fluxless TCB solves the issues that standard TCB encounters with the flux.
The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
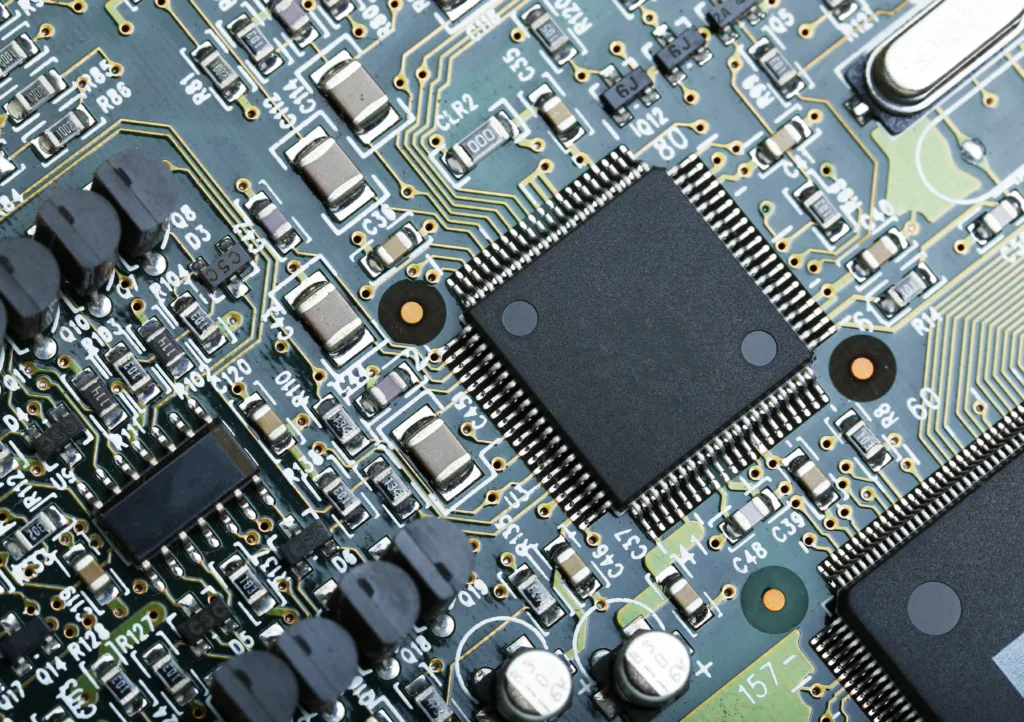
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
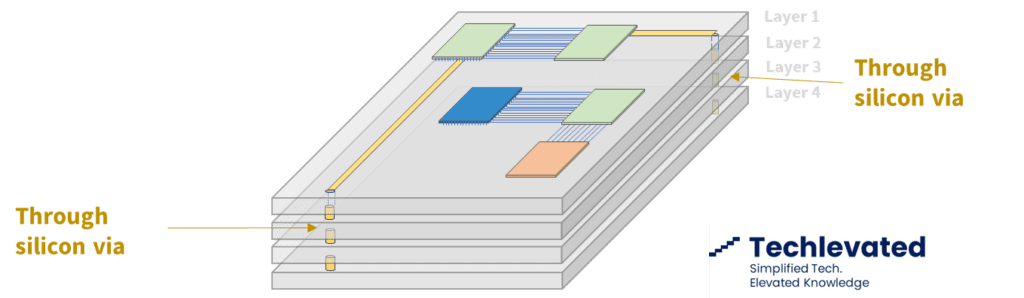
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
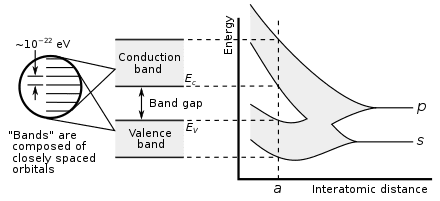
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
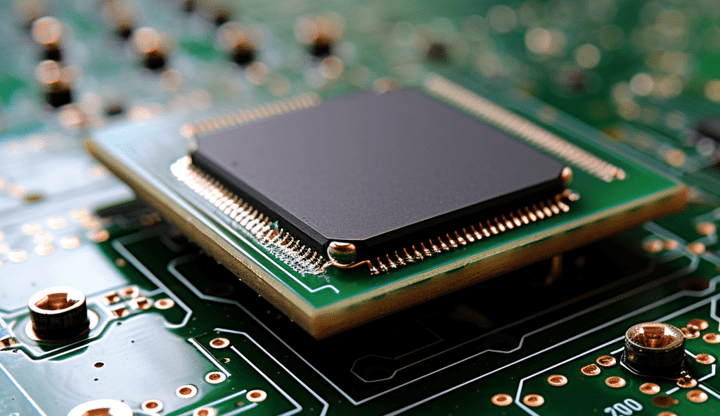
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.