The metal pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent metal interconnect lines on an integrated circuit (IC). Since transistors evolved into 3D strucrures, this measurement has lost significance.
Front-end vs Back-end in Semiconductors: 7 Differences
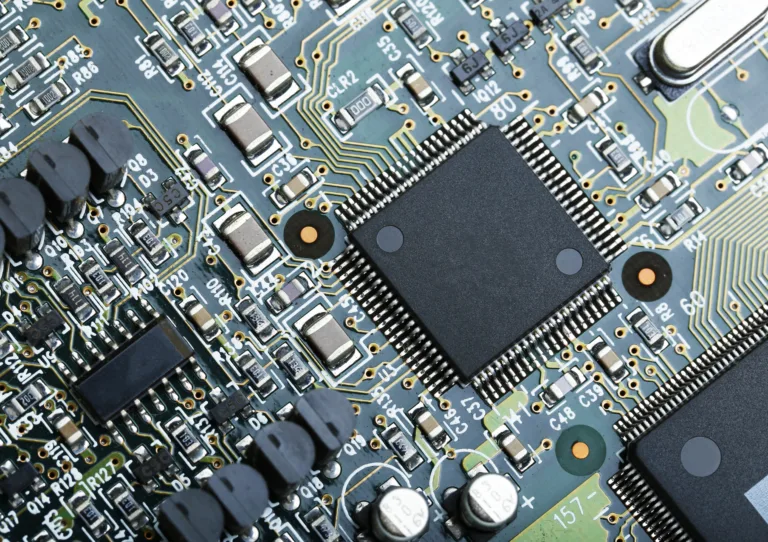
The front-end and back-end are highly interdependent. A constant feedback loop between front and back-end engineers is necessary to improve manufacturing yields.
Through-Silicon Via: Interconnecting Chip Layers
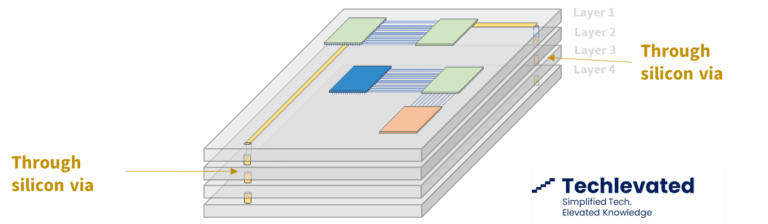
Built directly into the silicon, through silicon vias (TSV) facilitate 3D IC integration and allow for more compact packaging. They have become the default solution to interconnect different chip layers or to stack chips vertically.
SiC vs GaN Transistors
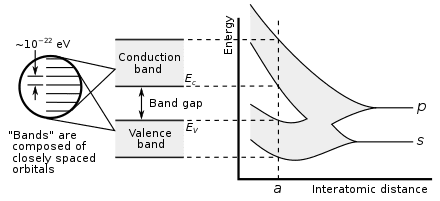
Silicon carbide (SiC) is used in electric vehicles due to its wide bandgap and great thermal conductivity. Gallium nitride (GaN) shares many characteristics with SiC while also minimizing RF noise.
Will GPUs Replace CPUs? Understanding Core Differences
GPU vs CPU is a parallelization vs complexity dilemma. While GPUs can manage very large parallel calculations, they struggle with linear, more heterogeneous tasks, where CPUs excel.
Direct-to-Chip Cooling In The Data Center
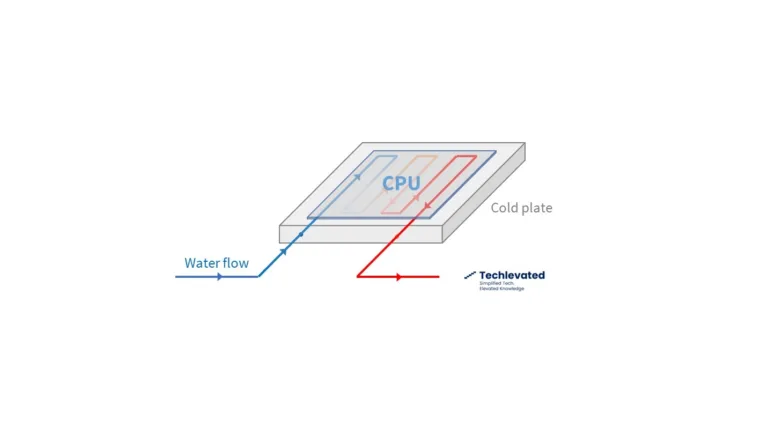
AI workloads require more server density and generate more heat. Direct-to-chip liquid cooling is emerging as the preferred cooling solution for AI with leaders like Meta, Google or Equinix adopting it.
The CFET Transistor: Shrinking Nodes Beyond 2030
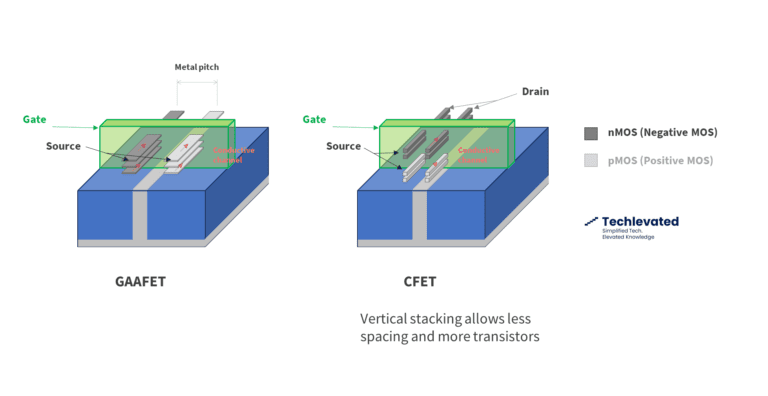
The move to CFET vs GAAFET marks a switch from horizontally stacked transistors to vertically stacked ones. This will allow further shrinking of semiconductor patterns and the advancement of Moore´s Law.
GAAFET vs FinFET: “Transistoring” to All-Around Nanosheets
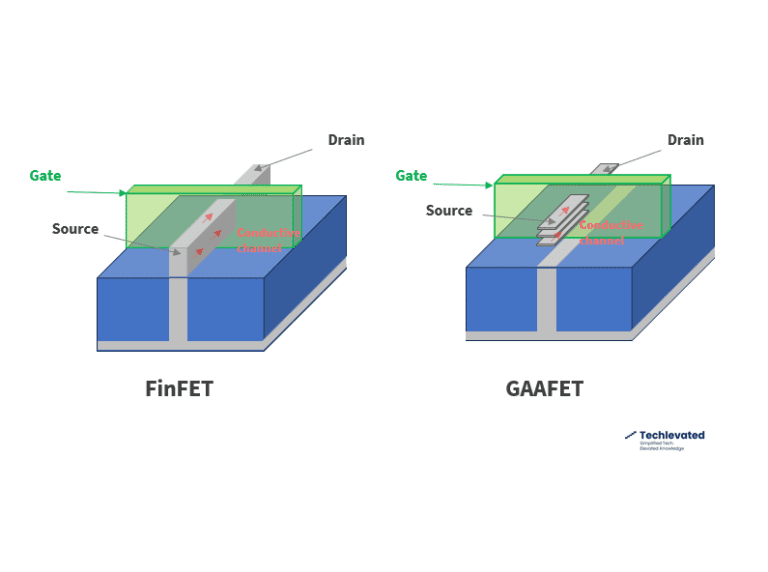
GAAFET vs FinFET marks an advancement in multigate transistors, shifting the conducting channel from vertical fins to nanosheets.
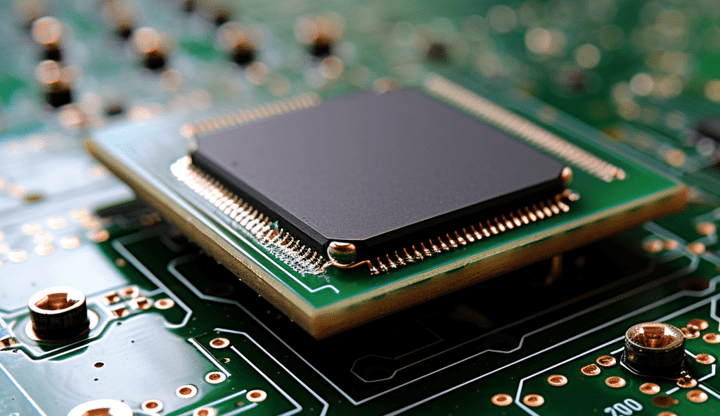
Wire Bond vs Flip-Chip: 7 Differences
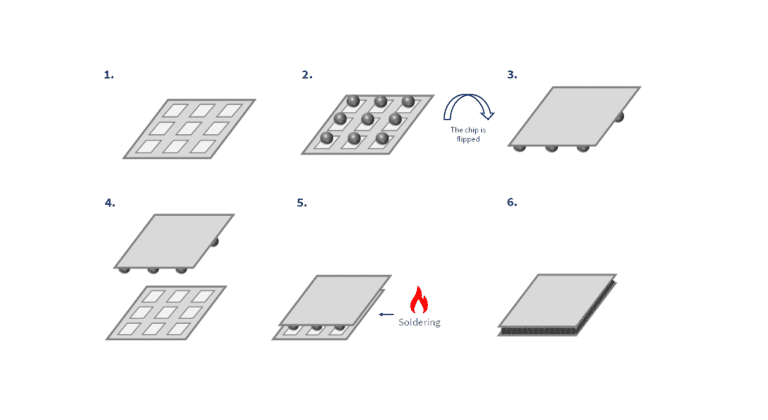
Wire bonding is a cheap and reliable semiconductor packaging method- Flip-chip is an advancement, creating more dense interconnections and allowing 3D vertical stacking.
Understanding Fab Yield in Semiconductors

Fab yield refers to the percentage of working chips in a semiconductor wafer. If a fab can’t meet the requirements, customers will switch to another provider.

